This is how it works if you want to continue on another device
To save your progress if you want to continue on another device, there are several options. Copy or email a link, or read provided QR-code.
When you started the course, you will be able to continue on another device.
-
Read QR-code
Scan the following QR-code with your phone to continue where you left.
-
Copied
- Or email the link to yourself
Count with CLIMB
CLIMB is a tool for Nordic conditions that calculates biodiversity within a geographical area.
CLIMB has been developed for such quantification to primarily be applied in case of land use change, i.e. in industries such as energy, material extraction, infrastructure and urban planning. CLIMB is developed to support informed land use decisions in line with EU and global biodiversity targets and new frameworks in finance and accounting.


The calculation model CLIMB has been developed by the company Ecogain in collaboration with 12 project partners from the business sector who have funded and driven the initiative by participating in the steering committee, where ongoing decisions regarding the model’s direction were made and important trade-offs were considered. Ecogain has acted as the project leader and coordinating partner for the collaboration and progress of the project.

The network Business@Biodiversity Sweden is facilitated by Ecogain. The network includes around 30 major players in the Swedish business sector who are united in their interest to implement efforts for biodiversity preservation in their operations. It was during one of the network’s meetings in 2018 that the idea for CLIMB began.
When can CLIMB be used?
Quantify biodiversity within an area
CLIMB can calculate the current level of biodiversity within an area. The result of the calculation provides a quantity of CLIMB units.
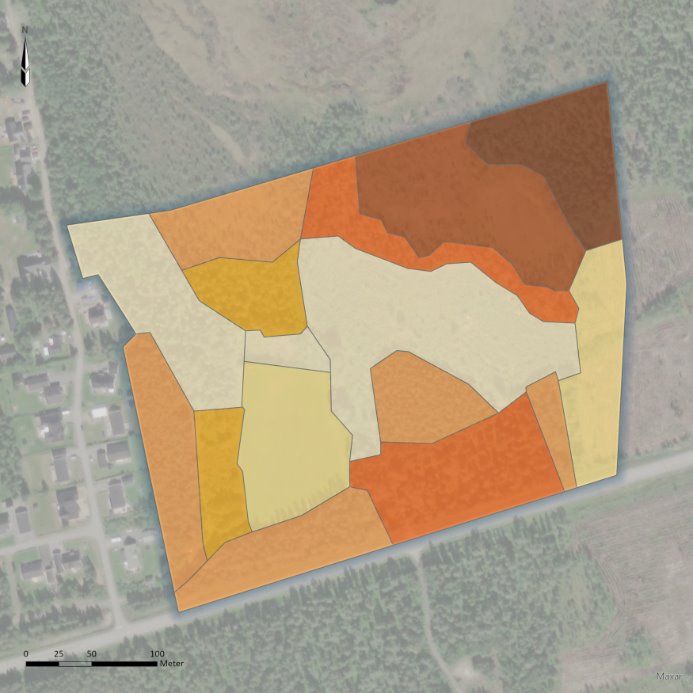
Example area where the CLIMB calculation resulted in 70 CLIMB units.
Investigation of different alternatives
CLIMB can be used to investigate and compare different location and layout designs within an area. If a CLIMB calculation is performed for two alternative designs, the results from the calculations can easily be compared with each other.
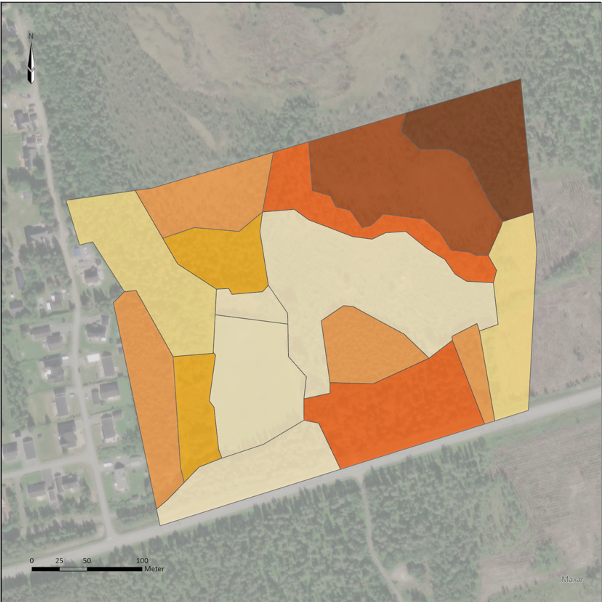
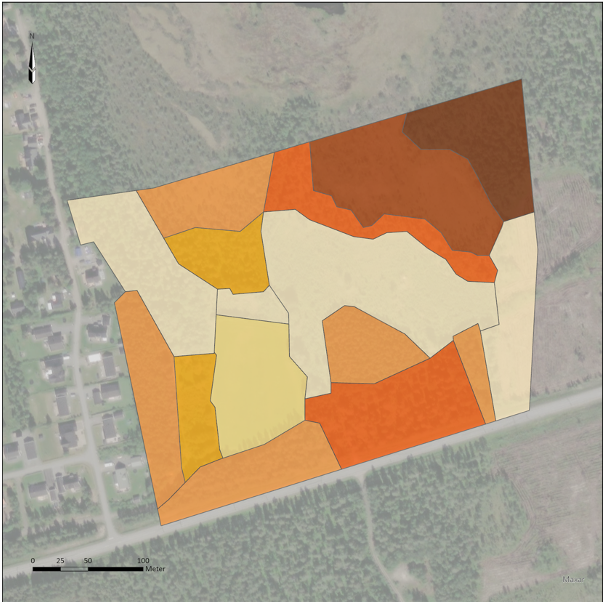
Two different designs of the same example area where the CLIMB calculation resulted in values of 64 and 69 CLIMB units, respectively.
Evaluate the overall impact of a project
The result of the CLIMB calculation can also provide an overview of a project’s overall environmental impact – how does biodiversity change as a result of the planned activity? The result can serve as the basis for compensation measures, which in turn could involve investments in nature elsewhere.
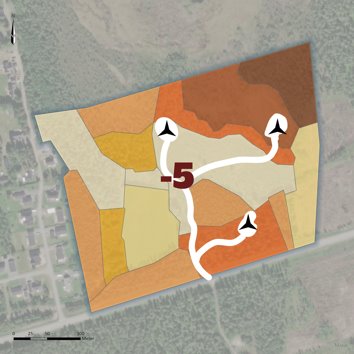
Example layout for a wind farm where the CLIMB calculation resulted in -5 CLIMB units.
Apply and demonstrate measures according to the mitigation hierarchy
CLIMB can also be used to apply and demonstrate measures according to the mitigation hierarchy: avoid, minimize, restore, and offset.
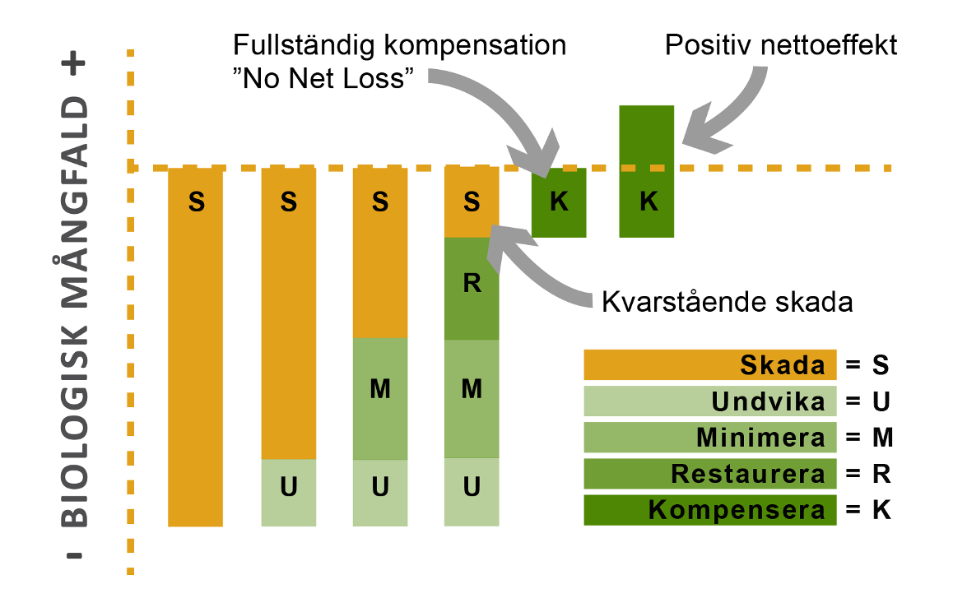
The mitigation hierarchy is a stepwise process that involves avoiding, minimizing, restoring, and offsetting for the impact on biodiversity.
Setting and measuring progress towards strategic goals
Many businesses have long been searching for a method to set biodiversity goals and then be able to follow up on such a goal. CLIMB is currently being used by several project partners to track progress towards their goals of increased biodiversity.

Serve as the basis for certification and reporting
CLIMB provides an excellent foundation for certification and reporting, and the steering committee is engaged in ongoing dialogues with various bodies. For instance, CLIMB can be used for reporting according to the upcoming EU requirements for sustainability reporting, CSRD, specifically the reporting standard ESRS E4 on biodiversity. It is also applicable within sustainability certification for construction and infrastructure projects such as BREEAM and Miljöbyggnad, where outdoor environments are now included in Miljöbyggnad 4.0.




Serve as the basis for requirements in financing and procurement
Another aspect is that CLIMB calculations can form the basis for the level of biodiversity performance an actor expects in financing or procurement. For example, when procuring rock material, an actor can set performance requirements for biodiversity in the same way they can set climate performance requirements.

Facilitate and clarify communication about biodiversity, both internally and externally
Numbers can indeed facilitate and clarify communication about biodiversity. A calculation with CLIMB can make it easier to understand the impact of different alternatives. It can also help to create a common understanding and direction within a company. By simplifying the impact a business has, CLIMB makes knowledge about biodiversity accessible to decision-makers.

